AWS CDK: Building a EventBridge scheduled Lambda that reads and writes to s3
- The CDK App that we will build
- Setting up the development environment
- Setting up the project
- Modifying the structure
- Defining the lambda function
- Define EventBridge Schedules and Lambda access permission
- Giving Lambda access to S3 bucket to read and write files
- Create a dependencies layer in Lambda CDK
- Upload the coordinates file to S3
- Writing the lambda app
- Deploy the CDK project
- Cleanup & Destroy the CDK project
AWS Cloud Development Kit, also known as CDK, is an Open Source Software Development Framework that is maintained by AWS.
CDK is supposed to be the umbrella SDK from AWS, which can also easily integrate with AWS SAM CLI and also AWS Chalice, two other open source SDKs that AWS provides.
Now, there are hundreds of simple guides that explains how to setup a simple Lambda app using CDK, but in this article we'll build a bit more complex example.
The CDK App that we will build
We'll build a Lambda app that runs at a specified time (using EventBridge). The Lambda app will read a file from S3 bucket that contains latitude and longiture stored in a CSV format. Then the Lambda app will fetch the sunrise & sunset times for those coordinates and save it to another file in S3.
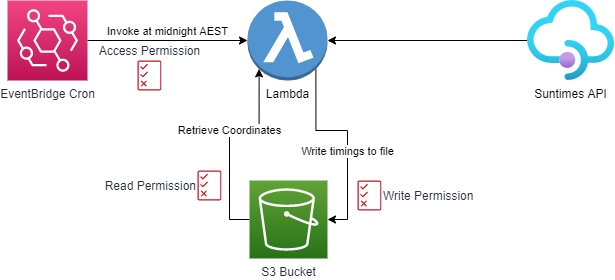
Components
Before we get into the weeds, let's look at what are the components that we will need to configure
- Sun timings API: We'll use a public API endpoint,
https://sunrise-sunset.org/api - EventBridge: An event generated at a specified time using Cron. This event will be used to invoke Lambda. EventBridge needs to have permissing to send target the Lambda function for invocation
- S3 Object with Coordinates: A file that contains a list of coordinates.
- S3 Object with output: This will be created by Lambda
- Lambda Function: A Lambda function that reads the list of coordinates from S3, fetches the sunrise / sunset times for them, converts them to JSON and saves it in S3. Lambda will require read & write permission to S3. To read and write from S3 we will use AWS Boto Library
Setting up the development environment
You need Docker & VSCode to be installed on your system for this guide. Download fromt he provided links and install.
Then follow the following steps.
Step 1: Install Python using these instructions.
Step 2: Install AWS CLI
Step 3: Configure AWS & AWS CLI
Step 4: Install and configure AWS CDK
Step 5: Bootstrap the CDK, i.e. configure your AWS account to be able to use CDK. To do this first run the following AWS CLI command
aws sts get-caller-identity
This will produce an output similar to below that will provide the AWS account number, and user-id.
{
"UserId": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"Account": "000000000000",
"Arn": "arn:aws:iam::000000000000:user/cloudbytes"
}
Then run the below command replacing account & userID
cdk bootstrap aws://<Account>/<Region>
You can get your default region by running
aws configure get region
Setting up the project
Create a new folder for the project, CDK requires an empty folder to initialise
mkdir cdk-tutorial
cd cdk-tutorial
After that, create a new CDK project by running
cdk init app --language python
appin the above is a template, don't change it
This will produce a bunch of files in the below structure
├── README.md
├── app.py
├── cdk.json
├── cdk_tutorial
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── cdk_tutorial_stack.py
├── requirements.txt
├── setup.py
└── source.bat
It will also create a virtual environment, to active run the below on Linux / MacOS
source .venv/bin/activate
Or on Windows, run
.venv\Scripts\activate.bat
Then finally run the below to install the project dependencies,
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
These are the libraries used by your project, not the actual Lambda app. We will define that later
Modifying the structure
Now the above initialisation has created 3 important files
app.py: This contains the initialisation of the app itself. This doesn't require any change unless you are changing the name of the app itself.cdk_tutorial/cdk_tutorial_stack.py: This is where we will define our app construct, i.e. the services that we will use, the permissions that we need, etc.setup.py: This contains certain project information such as libraries etc.
Adding Lambda Handler
Create a folder named lambda and under the folder create two files 1. __init__.py: Should be an empty file 2. index.py: Leave the contents blank for now
Defining the lambda function
Go to cdk_tutorial/cdk_tutorial_stack.py, and change the imports as per below
from aws_cdk import core as cdk, aws_lambda, aws_events_targets as targets, aws_events as events, aws_s3 as s3
import subprocess
Then change the main program as per below
# app.py
class CdkTutorialStack(cdk.Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: cdk.Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# Define a lambda function
lambdaFn = aws_lambda.Function(
self,
"cdk-tutorial",
code=aws_lambda.Code.from_asset("lambda"),
handler="index.main",
runtime=aws_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
layers=[self.create_dependencies_layer(self.stack_name, "lambda/index")],
)
Here we use code variable to import our code from lambda folder, then define Lambda handler to be main() method under index.py file by using handler="index.main".
We also define the runtime to be Python 3.10 and a layer that is explained later.
Define EventBridge Schedules and Lambda access permission
Add the below code under where we defined lambda function
rule = events.Rule(
self,
"Run Daily at 21:30 hrs UTC",
# UTC + 0 time. ~3 AM IST
schedule=events.Schedule.cron(minute="30", hour="21", week_day="*", month="*", year="*"),
)
rule.add_target(targets.LambdaFunction(lambdaFn))
This simple definition has two parts 1. Where we define an Eventbridge rule that runs everyday as 9:30 PM UTC. The event schedule is always expressed in UTC timezone 2. We add a target to the lambda function that we created, lambdaFn
That's it, two statements to create and then give permission to EventBridge to invoke a Lambda function.
Giving Lambda access to S3 bucket to read and write files
For this you need the name of the bucket that you want access to, in this example let's use cloudbytes-dev, you can replace it with bucket of your choice that you are using.
To provide access, we first define the bucket construct and then grant read & write permission as per below
my_bucket = s3.Bucket.from_bucket_name(self, "Bucket", "cloudbytes-dev")
my_bucket.grant_read_write(lambdaFn)
Create a dependencies layer in Lambda CDK
For our program we are going to use Python's requests library, however, this is not available by default on Lambda, so we need to upload this while creating our project.
To do that, we need to do two things, first, add the below function in your app.py
def create_dependencies_layer(self, project_name, function_name: str) -> aws_lambda.LayerVersion:
requirements_file = f"requirements.app.txt"
output_dir = f".build/app"
if not os.environ.get("SKIP_PIP"):
subprocess.check_call(f"pip install -r {requirements_file} -t {output_dir}/python".split())
layer_id = f"{project_name}-{function_name}-dependencies"
layer_code = aws_lambda.Code.from_asset(output_dir)
return aws_lambda.LayerVersion(self, layer_id, code=layer_code)
Then create a file named requirements.app.txt in your project root (where requirements.txt is) and add the following in that file
requests==2.26.0
boto3==1.18.24
(Optional) Install these in your virtual environment by running
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.app.txt
Upload the coordinates file to S3
Copy the below in a file and name it coordinates.csv
latitude,longitude
-33.865143,151.209900
22.572645,88.363892
Upload this file to the S3 bucket that you are going to use
Writing the lambda app
Go back to you lambda folder that we craete earlier and opent he index.py file
Add the following code to the file
from botocore import endpoint
import requests
import os
import boto3
import csv
import json
def main(event, context):
s3 = boto3.client("s3")
bucket = "cloudbytes-dev"
file_name = "coordinates.csv"
# Download the coordinate files from S3
s3.download_file(bucket, file_name, f"/tmp/{file_name}")
coordinates = []
with open(f"/tmp/{file_name}", "r") as file:
rows = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in rows:
endpoint = f"https://api.sunrise-sunset.org/json?lat={row['latitude']}&lng={row['longitude']}"
response = requests.get(endpoint)
row["sunrise"] = response.json()["sunrise"]
row["sunset"] = response.json()["sunset"]
coordinates.append(row)
output_file = "suntimes.json"
with open(f"/tmp/{output_file}", "w") as file:
file.write(json.dumps(str(coordinates)))
# Upload the output file to S3
s3.upload_file(f"/tmp/{output_file}", bucket, f"{output_file}")
Deploy the CDK project
Before deploying we first need to synthesis (or generate the project CloudFormation template) by running
cdk synth
This will generate a lengthy CloudFormation output in the console.
Finally, we deploy the project by running
cdk deploy
If asked for a confirmation, press Y to deploy.
Now you can go to your AWS console, go to lambda section and test the function.
Cleanup & Destroy the CDK project
We created several resources and policies as part of this tutorial, instead of deleting them one by one, just run
cdk destroy
This will clean up the project competely.
And this is how you build a complex Lambda application on AWS