Running Lambda Functions in a VPC with AWS CDK in Python
We have created several lambda functions that are running in AWS owned default VPC. However, this means if you need to access any resources in your AWS account, the access is over the internet.
Hence, in several scenarios, you may need to run your lambda functions in a VPC, e.g.:
- Access to private resources such as EC2, RDS, etc: If your Lambda function needs to access private resources inside a VPC (such as an RDS database that is not publicly accessible, an ElastiCache cluster, or an EC2 instance), you must place it inside the same VPC.
- Connecting to internal APIs or services: If you have private APIs or services hosted inside the VPC, your Lambda function needs to be in the same VPC to call them.
- Using VPC Interface Endpoints (AWS PrivateLink): If your Lambda function needs to interact with AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, or SQS using VPC interface endpoints (AWS PrivateLink) for enhanced security (instead of going over the public internet).
This article will show you how to create a lambda function that is running in a VPC using AWS CDK in Python.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have AWS CDK and SAM CLI installed.
- If needed create a new CDK application.
- We need a VPC with private subnet. You can follow this article to create a VPC with private subnet.
Creating a Lambda function in a VPC
Before we create a Lambda function, we need appropriate VPC and subnets. If you need to create a VPC, you can follow this article to create a VPC with private subnet.
We will create the lambda function in the private subnet of the VPC. The following code creates a Lambda function in a VPC.
# filename: cdk_app/my_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_ec2 as ec2,
aws_lambda_python_alpha as python_lambda,
aws_lambda as lambda_,
)
from constructs import Construct
class MyStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# 👇🏽 Enter the appropriate values
subnet_id = "subnet-00000000000000000"
vpc_id = "vpc-00000000000000000"
vpc = ec2.Vpc.from_lookup(
self,
"VPC",
vpc_id=vpc_id,
)
# Get the specific subnet by its ID
private_subnet = ec2.Subnet.from_subnet_id(self, "PrivateSubnet", subnet_id)
# Define the Lambda function within the specific subnet
my_vpc_lambda = python_lambda.PythonFunction(
self,
"MyVpcLambdaFunction",
entry="cdk_app/fn",
runtime=lambda_.Runtime.PYTHON_3_12,
index="index.py",
handler="handler",
vpc=vpc,
vpc_subnets=ec2.SubnetSelection(subnets=[private_subnet]),
)
Explanation
- VPC: We are using the
from_lookupmethod to get the VPC by its ID. This allows us to reference an existing VPC in your AWS account. - Subnet: We are using the
from_subnet_idmethod to get the subnet by its ID. This allows us to reference an existing subnet in your AWS account. - Lambda Function: We are using the
PythonFunctionconstruct to create a Lambda function. Thevpcparameter specifies the VPC in which the Lambda function will run, and thevpc_subnetsparameter specifies the subnets in which the Lambda function will run. - Entry: The
entryparameter specifies the directory where the Lambda function code is located. In this case, it is in thecdk_app/fndirectory. - Runtime: The
runtimeparameter specifies the runtime environment for the Lambda function. In this case, it is Python 3.12. - Index: The
indexparameter specifies the name of the file that contains the Lambda function code. In this case, it isindex.py. - Handler: The
handlerparameter specifies the name of the function that will be called when the Lambda function is invoked. In this case, it ishandler.
You can deploy the stack using the following command:
cdk deploy
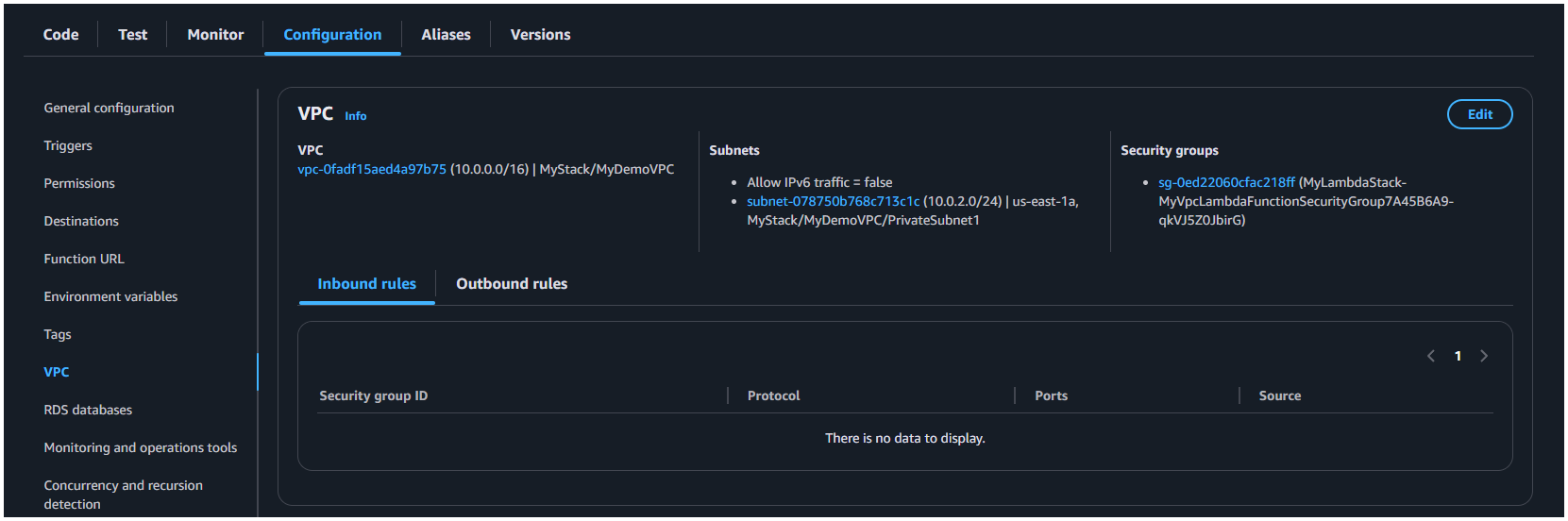
This will create a Lambda function in the specified VPC and subnet. You can check the AWS Management Console to verify that the lambda function is created correctly and is running in the specified VPC and subnet in the VPC section of Configuration.