How to Import Stack Output from another stack
In the previous article, I explained how to export data from a stack using Outputs. Outputs are a way to export specific values from a stack. These values can be anything: an S3 bucket name, a database connection string, or even a computed value.
Output can be imported by another stack as a reference helping you access resources created in another stack.
How to import an Output in CDK?
While printing the outputs is useful, the real power of Outputs is when you use them in other stacks.
We need to use the Fn.import_value function to import the value of an Output. This function is available in the aws_cdk module.
Export the Output
Let's first create the S3 bucket stack from the previous article. Create a new file called cdk_app/s3_stack.py and add the following code to it:
# filename: cdk_app/s3_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_s3 as s3,
RemovalPolicy,
)
from aws_cdk import CfnOutput # 👈🏽 Import the CfnOutput class
from constructs import Construct
class S3Stack(Stack):
BUCKET_ID = "MyS3Bucket"
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
myBucket = s3.Bucket(self, id=self.BUCKET_ID, removal_policy=RemovalPolicy.DESTROY)
# 👇🏽 Output the bucket ARN
CfnOutput(self, id="S3BucketARN", value=myBucket.bucket_arn, export_name="MyS3BucketARN")
In the above example, we are creating an S3 bucket and then exporting its ARN as an Output.
Import the Output
Now, let's create a new stack that will import the S3 bucket ARN. Create a new file called cdk_app/lambda_stack.py and add the following code to it:
# cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
aws_s3 as s3,
)
from aws_cdk import Fn # 👈🏽 Import the Fn class this contains the import_value method
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
bucket_arn = Fn.import_value("MyS3BucketARN")
myBucket = s3.Bucket.from_bucket_arn(self, id="MyImportedBucket", bucket_arn)
_lambda.Function(
self,
id="MyLambdaFn",
# 👇🏽 Pass the bucket name as an environment variable
environment={"BUCKET_NAME": myBucket.bucket_name},
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("./"), # 👈🏽 Use the current directory as the source
handler="index.main", # 👈🏽 Filename is index.py and the function is called main
)
In the above example, we imported the S3 bucket ARN using the Fn.import_value method. We then used the from_bucket_arn method to create a reference to the S3 bucket.
We then created a Lambda function and passed the bucket name as an environment variable.
Now we create the Lambda function in the cdk_app/lambda/index.py file:
# cdk_app/lambda/index.py
import os
bucket_name = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"]
def main(event, context):
print(f"Bucket Name: {bucket_name}")
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": bucket_name,
}
Deploy the stacks
Now, let's modify our app.py file to deploy both stacks:
# app.py
import aws_cdk as cdk
from cdk_app.s3_stack import S3Stack
from cdk_app.lambda_stack import LambdaStack
app = cdk.App()
# LambdaStack depends on S3Stack
s3_stack = S3Stack(app, "S3Stack")
lambda_stack = LambdaStack(app, "LambdaStack")
# 👇🏽 Add the dependency to ensure S3Stack is deployed first
lambda_stack.add_dependency(s3_stack)
app.synth()
Note that we have added a dependency between the two stacks. This is because the Lambda function depends on the S3 bucket so we need to ensure that the S3 bucket is deployed first.
Now, run cdk deploy --all to deploy the stacks.
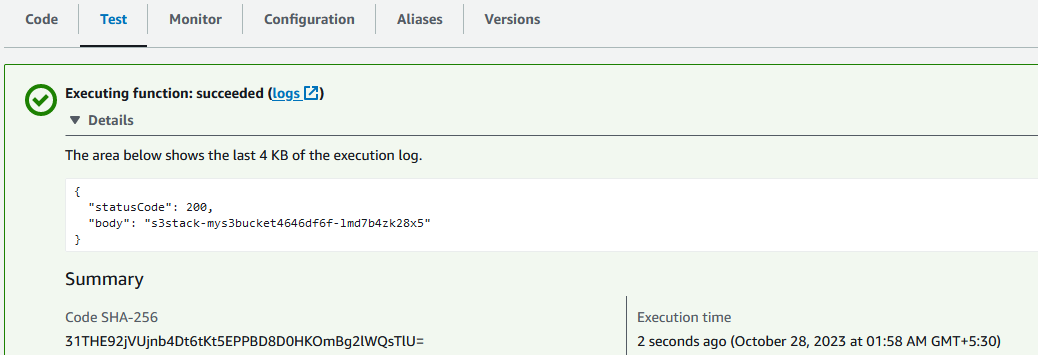
Testing the stacks
Go to the AWS Console and run the Lambda function. You will see the following output: