How to create a lambda function using AWS CDK in Python
The easiest way to create a lambda function using AWS CDK is to use the Function construct from the aws_lambda module. Let's see how to use it.
Create a simple lambda function
# filename: cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
)
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
inline_code = """
def handler(event, context):
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": "Hello from Lambda!"
}
"""
# 👆🏽 formatting & indentation is not a mistake
my_lambda = _lambda.Function(
self,
id="MyLambda",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="index.handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_inline(inline_code),
)
You can create the app by modifying the app.py file as follows:
# filename: app.py
import aws_cdk as cdk
from cdk_app.lambda_stack import LambdaStack
app = cdk.App()
lambda_stack = LambdaStack(app, "LambdaStack")
app.synth()
To deploy, run cdk deploy.
Once deployed, you can go to the AWS Console and check the lambda function. You should see the following:
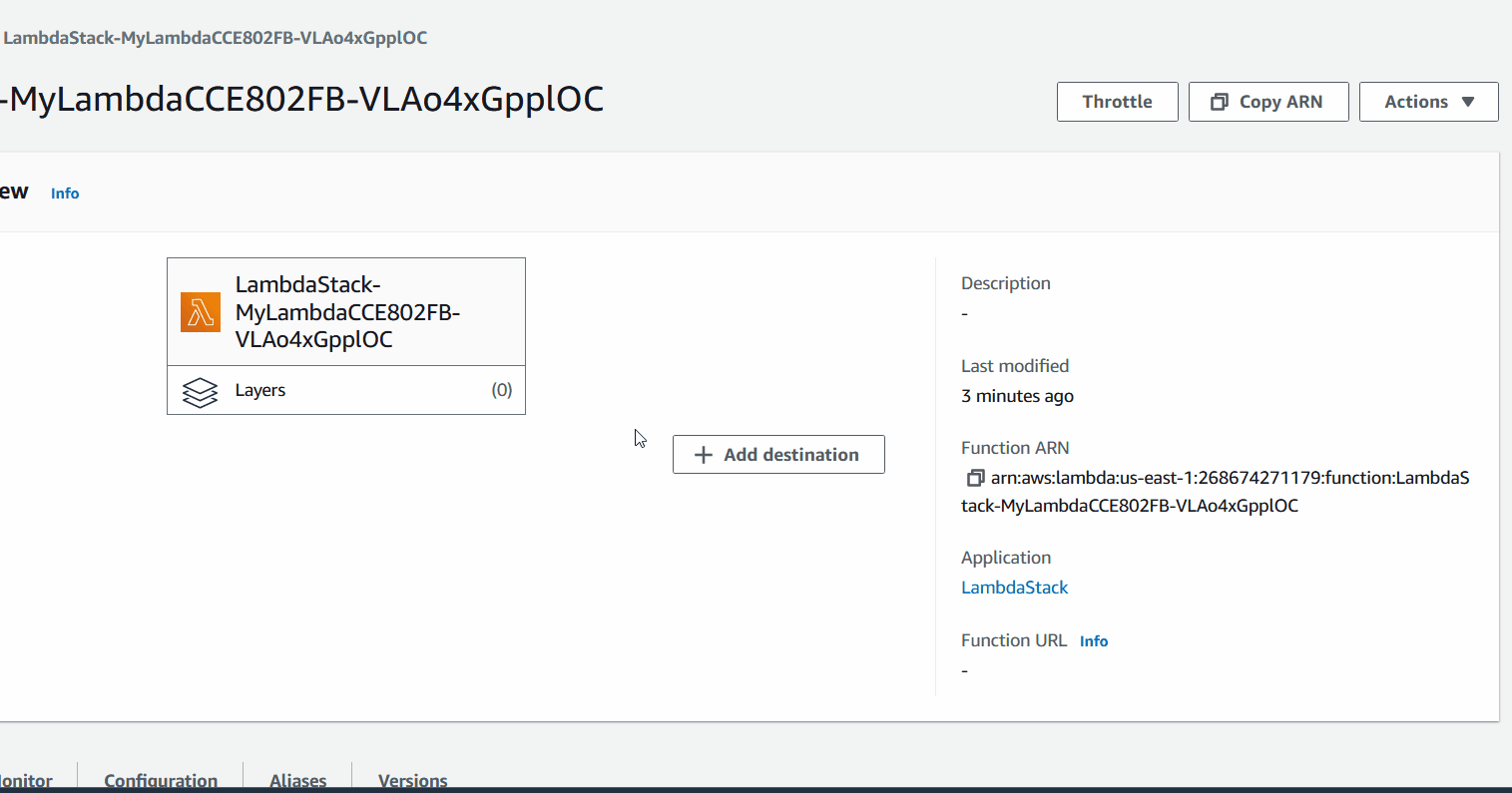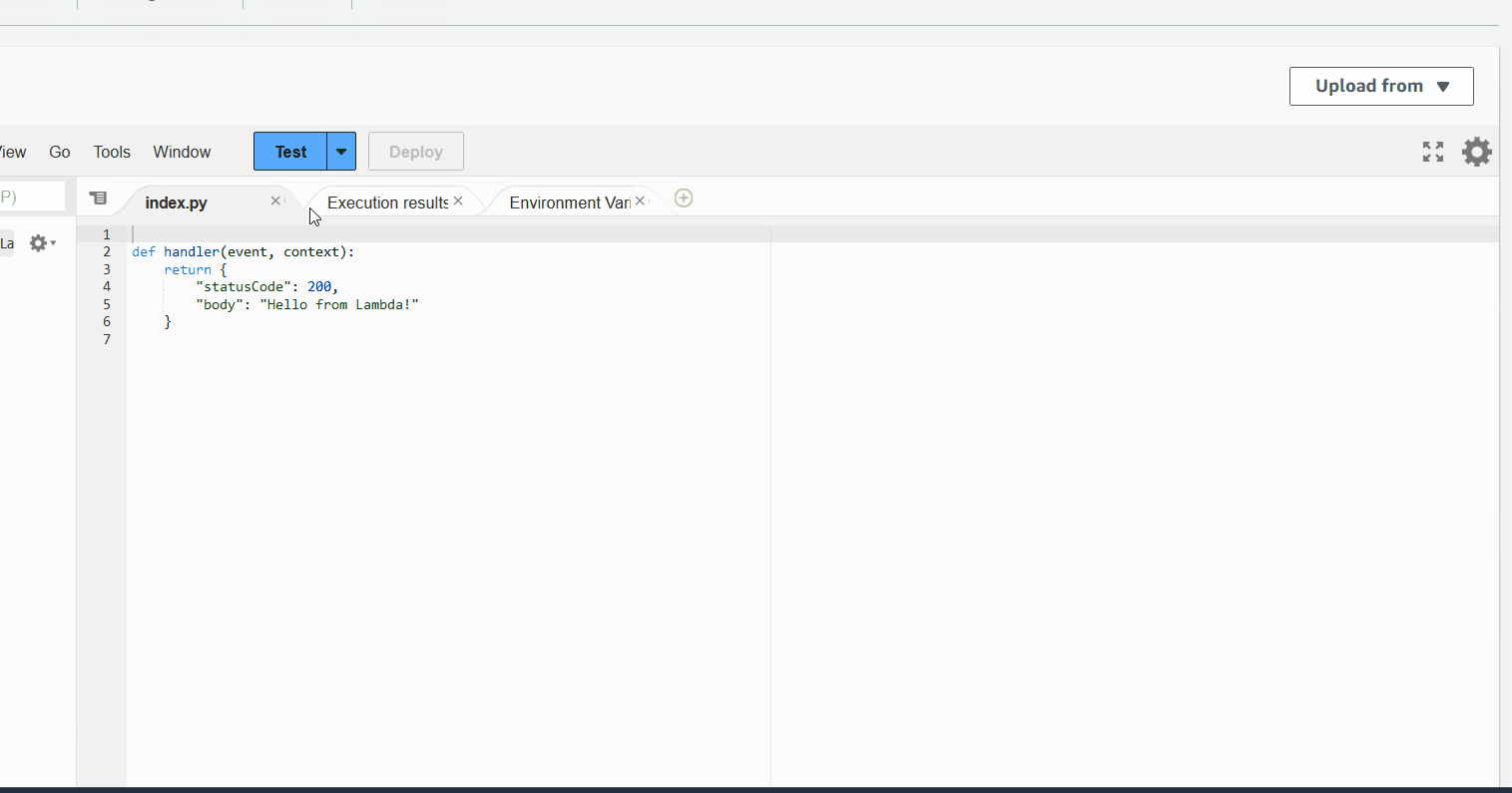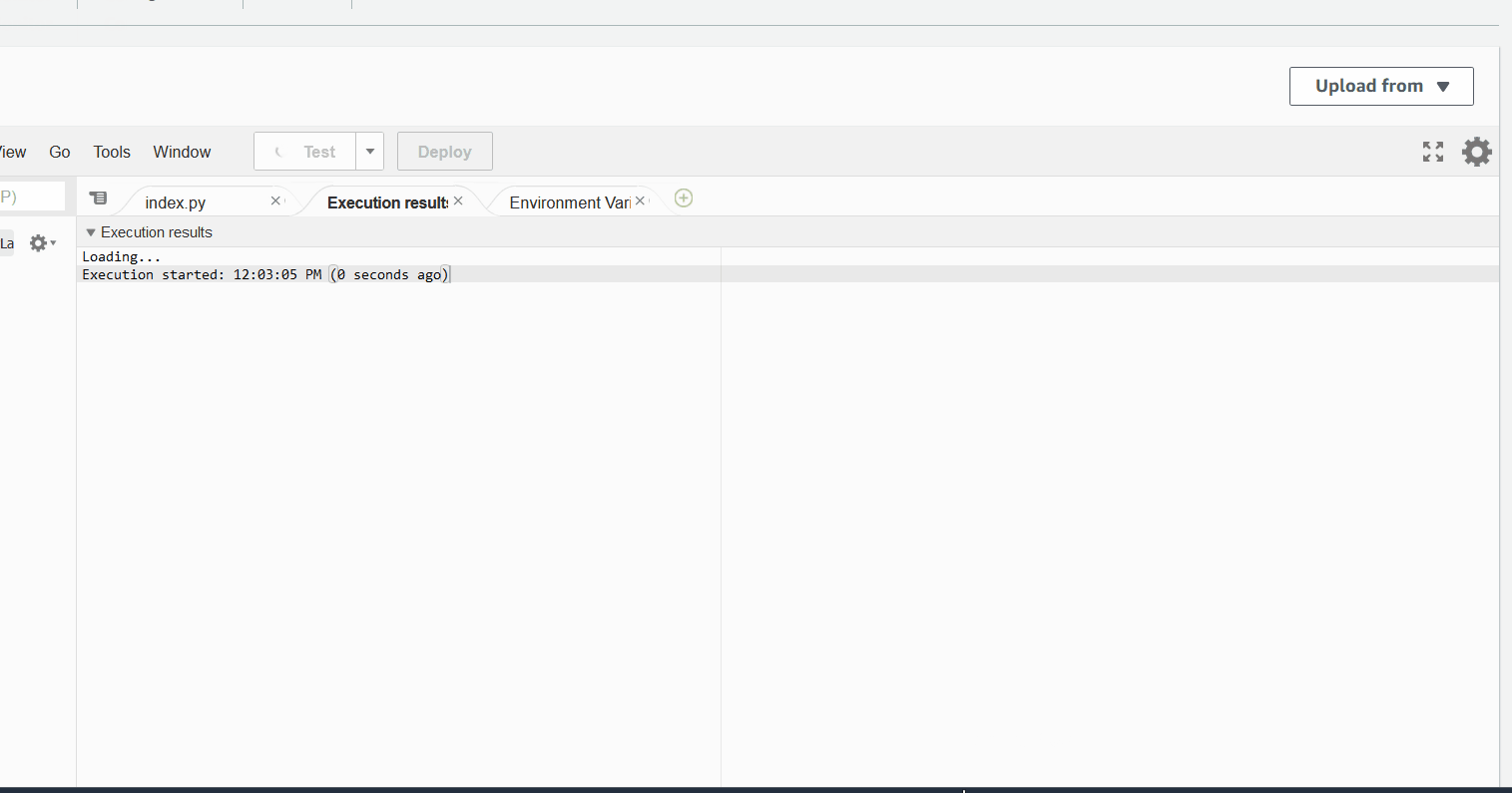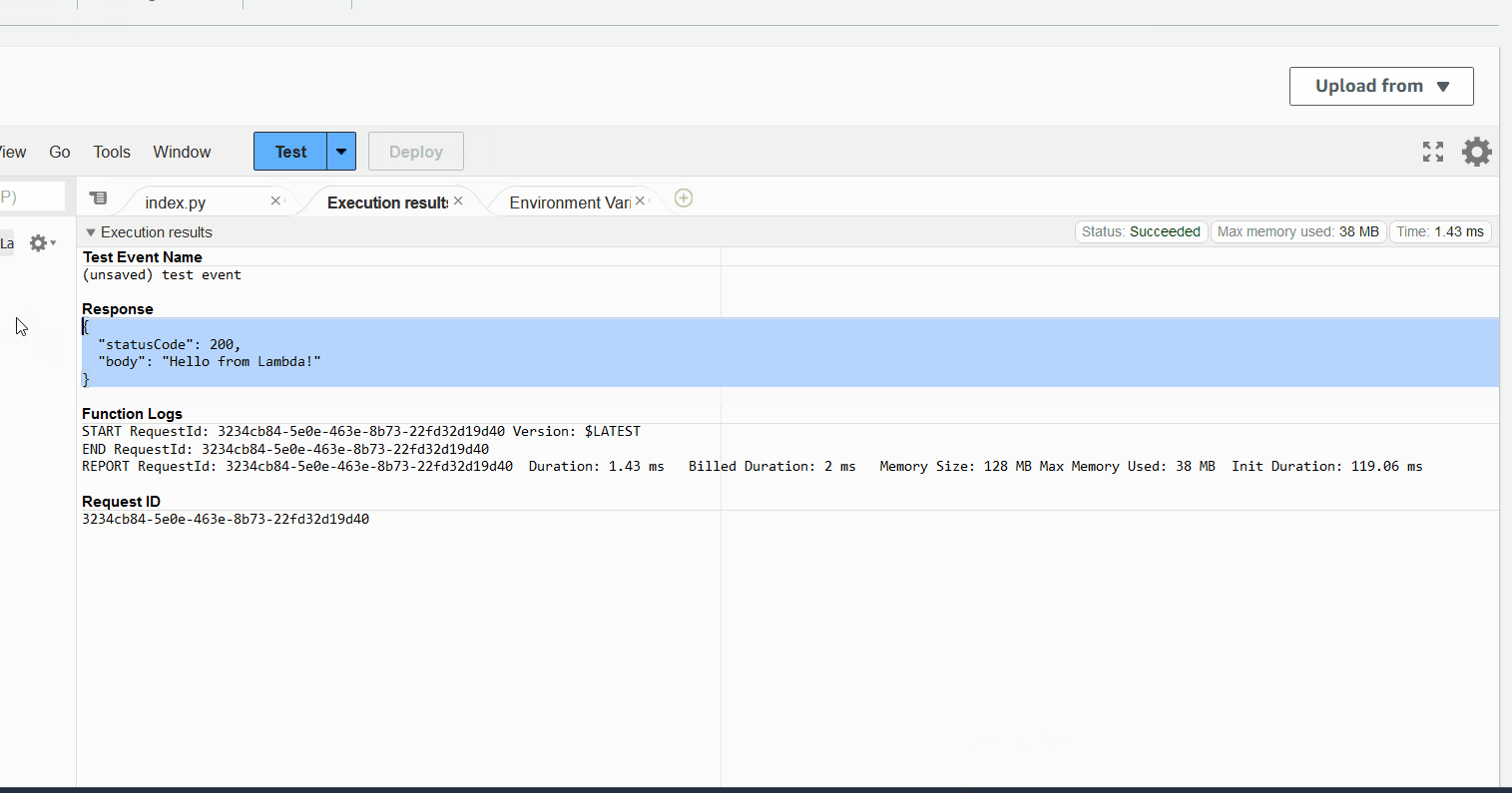
What's happening here?
We used what is known as an inline code to create the lambda function. Effectively, the code we want to execute is passed as a string to the code property of the Function construct.
The Function construct takes the following parameters:
scope: The scope in which the construct is created. In our case, it is theLambdaStackclass.id: The ID of the construct. This ID is used within CDK to uniquely identify the construct. It is also used as the logical ID in CloudFormation templates.runtime: The runtime environment for the lambda function. In our case, it is Python 3.10. Other versions of Python are also supported. You can also use other runtimes such as Node.js, Java, Go, etc.handler: The name of the handler function. In our case, it isindex.handler. This means that thehandlerfunction is defined in theindex.pyfile.code: The code to execute. In our case, it is theinline_codevariable.
But using inline code is not the best way to create a lambda function. It is fine for simple demonstrations, but for anything more complex, you should use a file or a Docker image. Let's see how to do that.
Create a lambda function from a file
To create a lambda function from a file, you need to use the Code.from_asset method. This method takes the path to the file as an argument.
Now one important point, the lambda code needs to be in its own directory. So, you need to create a directory and put the lambda code in that directory.
E.g. in our case, we will create a cdk_app/lambda directory and create a file named index.py in that directory. The contents of the file will be as follows:
# filename: cdk_app/lambda/index.py
def handler(event, context):
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": "Hello from Lambda!",
}
Now, we can create the lambda function as follows:
# filename: cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
)
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
my_lambda = _lambda.Function(
self,
id="MyLambda",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="index.handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("cdk_app/lambda"),
)
Notice that we have used the Code.from_asset method to create the lambda function. We have passed the path to the lambda directory as an argument to the method.
Now, when you run cdk deploy, you will see that the lambda function is created from the index.py file.
Set environment variables
You can set environment variables for the lambda function by using the environment property of the Function construct.
# filename: cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
)
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
my_lambda = _lambda.Function(
self,
id="MyLambda",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="index.handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("cdk_app/lambda"),
# 👇🏽 set environment variables
environment={
"ENVIRONMENT": "PROD",
},
)
Set memory size and timeout
By default lambda provide 128 MB of memory and 3 seconds of timeout. That means if your lambda function takes more than 3 seconds to execute, it will timeout.
If your lambda function requires more memory or more time, you can set the memory_size and timeout properties of the Function construct.
# filename: cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
Duration,
)
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
my_lambda = _lambda.Function(
self,
id="MyLambda",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="index.handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("cdk_app/lambda"),
# 👇🏽 set memory size and timeout
memory_size=256,
timeout=Duration.seconds(10),
)
Additional resources for lambda functions
Or learn some advanced methods on how to create lambda functions: