How to create a Lambda function in a Custom Docker image using AWS CDK in Python
In previous posts we looked at how to create using AWS CDK:
- Default Lambda function,
- Lambda function with Python dependencies using a Lambda layer
- Lambda function with Python dependencies that uses AWS provided Docker image
- Lambda function using a AWS ECR Docker image
But what if you need something more custom? We can use a similar approach to the previous post, but it requires a bit more work.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have AWS CDK and SAM CLI installed.
- If needed create a new CDK application.
Create a Lambda function using a custom Docker image
We will need to do the following:
- Create the
Dockerfile - Create a
requirements.txtfile to specify the Python packages to be installed. - Add AWS Lambda Runtime Interface Client (RIC) to the Dockerfile.
- Write the lambda function.
- Create the lambda stack.
1. Create the Dockerfile
Let's create a lambda directory in cdk_app to store the files for this function.
# filename: cdk_app/lambda/Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu:latest
ARG FUNCTION_DIR="/function"
# 👇🏽 Install Python and pip
RUN apt update -y
RUN apt install -y python3 python3-pip
# 👇🏽 Copy the rest of the application
RUN mkdir -p ${FUNCTION_DIR}
COPY . ${FUNCTION_DIR}
# 👇🏽 Set working directory
WORKDIR ${FUNCTION_DIR}
# 👇🏽 Install dependencies
# A target directory is required since latest versions of Ubuntu have implemented PEP 668
# which prevents pip from installing packages system-wide.
RUN python3 -m pip install --target ${FUNCTION_DIR} -r requirements.txt
# 👇🏽 Install AWS Lambda Runtime Interface Client
RUN python3 -m pip install --target ${FUNCTION_DIR} awslambdaric
# 👇🏽 Define the entrypoint
ENTRYPOINT ["python3", "-m", "awslambdaric"]
# 👇🏽 Set the handler to be used by the Lambda runtime
CMD ["index.handler"]
Within this image we have:
- Used the latest Ubuntu as the base image. This could be changed to a different image if needed.
- We ensure that Python and pip are installed.
- Created a directory for the function code.
- Copied the function code into function directory.
- Installed the Python packages specified in the
requirements.txtfile in the function directory. - Installed the AWS Lambda Runtime Interface Client (RIC) in the function directory.
- Set the command to be executed when the container starts.
Note
- The RIC is required for the Lambda function to communicate with the Lambda runtime.
- The packages are installed in the function directory since the latest versions of Ubuntu have implemented PEP 668 which prevents pip from installing packages system-wide.
- The
ENTRYPOINTandCMDinstructions are used to specify the command to be executed when the container starts.
2. Create a requirements.txt file
Create a new file called requirements.txt in the cdk_app/lambda directory. Any Python packages that you may need to install can be added to this file.
requests
3. Create the lambda function
Within the lambda directory create a new file called index.py. This is the main Python file that will be executed by the Lambda function.
# filename: cdk_app/lambda/index.py
import requests
def handler(event, context):
response = requests.get("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1")
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": response.json()}
4. Create a lambda_stack.py file
We modify the lambda_stack.py file to create the CDK stack.
# filename: cdk_app/lambda_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
)
from constructs import Construct
class LambdaStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
fn = _lambda.DockerImageFunction(
self,
"LambdaFunction",
code=_lambda.DockerImageCode.from_image_asset("cdk_app/lambda"),
)
In the above code we use the DockerImageFunction construct to create the Lambda function. It takes the following arguments:
self: The construct itself.id: The unique identifier for the function.code: The Docker image code. In this case we are using theDockerImageCode.from_image_assetmethod to specify the path to the Docker image.environment: The environment variables for the function. This is not required but is useful for testing purposes.
Compared to previous examples, we don't need to identify the handler function as this is specified in the Dockerfile.
Now finally, let's initialise the stack by creating the app.py file.
# filename: app.py
import aws_cdk as cdk
from cdk_app.lambda_stack import LambdaStack
app = cdk.App()
lambda_stack = LambdaStack(app, "LambdaStack")
app.synth()
To deploy the stack, run cdk deploy.
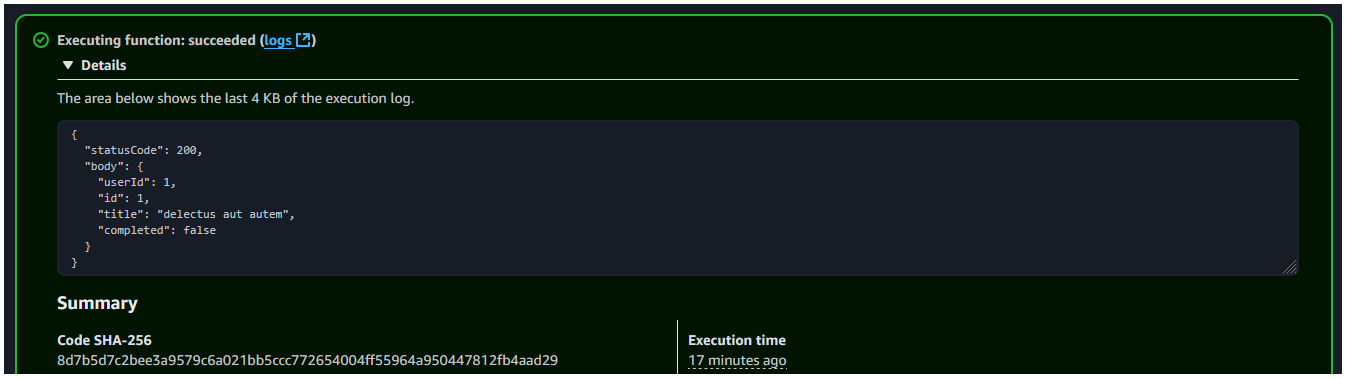
When the lambda function is deployed, you can go to the console and test the function. It should show the below output.