Granting Lambda function permission to access DynamoDB using AWS CDK in Python
Part of the serverless design pattern is to have a Lambda function that interacts with a DynamoDB table. The DynamoDB can be access only through APIs using appropriate credentials. In this article, we will look at how to grant a Lambda function permission to access a DynamoDB table using AWS CDK in Python.
Prerequisites
- Ensure that you have AWS CDK and SAM CLI installed.
- If needed create a new CDK application.
Granting Lambda function permissions to access DynamoDB
We will need to do the following:
- Create an DynamoDB table and insert some data.
- Create a Lambda function.
- Grant the Lambda function permissions to access the DynamoDB table.
1. Create an DynamoDB table
First, let's create an DynamoDB table in the stack.
# filename: cdk_app/my_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_dynamodb as dynamodb,
RemovalPolicy,
)
from constructs import Construct
class MyStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# 👇🏽 Create a DynamoDB table
table = dynamodb.Table(
self,
"MyTable",
partition_key={"name": "pk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
sort_key={"name": "sk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
)
2. Create a Lambda function
We can create a simple Lambda function using any of the methods we have discussed in the previous posts. For this example we will use the CDK provided PythonFunction feature that allows us to specify the python dependencies in AWS Lambda with ease.
Step 1: First we install the aws-cdk.aws-lambda-python-alpha module:
pip install aws-cdk.aws-lambda-python-alpha
Step 2: Then we create a Lambda function. We can also pass the name of the bucket to Lambda through the environment variables.
# filename: cdk_app/my_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_dynamodb as dynamodb,
aws_lambda_python_alpha as python_lambda, # 👈🏽 This is the python lambda construct
aws_lambda as lambda_, # 👈🏽 This is needed for runtime
RemovalPolicy,
)
from constructs import Construct
class MyStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
table = dynamodb.Table(
self,
"MyTable",
partition_key={"name": "pk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
sort_key={"name": "sk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
removal_policy=RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
)
# 👇🏽 Create a Lambda function
fn = python_lambda.PythonFunction(
self,
"MyDynamoDBFunction",
entry="cdk_app/fn",
runtime=lambda_.Runtime.PYTHON_3_12,
index="index.py",
handler="handler",
)
Step 3: Now we write the Lambda function code:
# filename: cdk_app/fn/index.py
import requests
def handler(event, context):
response = requests.get("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1")
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": response.json()}
Step 4: Add the Python dependencies in the cdk_app/fn/requirements.txt file:
requests
boto3
3. Grant the Lambda function permissions to access the S3 bucket
Finally, we need to grant the Lambda function necessary permissions to access the DynamoDB table.
# filename: cdk_app/my_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_dynamodb as dynamodb,
aws_lambda_python_alpha as python_lambda,
aws_lambda as lambda_,
RemovalPolicy,
)
from constructs import Construct
class MyStack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
table = dynamodb.Table(
self,
"MyTable",
partition_key={"name": "pk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
sort_key={"name": "sk", "type": dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING},
removal_policy=RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
)
fn = python_lambda.PythonFunction(
self,
"MyDynamoDBFunction",
entry="cdk_app/fn",
runtime=lambda_.Runtime.PYTHON_3_12,
index="index.py",
handler="handler",
)
# 👇🏽 Grant the Lambda function access to the DynamoDB table
table.grant_read_write_data(fn)
In the above code, we use the grant_read_write_data method to grant the Lambda function read and write access to the DynamoDB table.
Alternatively, you can use the grant_read or grant_write methods to grant only read or write access respectively.
Accessing DynamoDB table using the Lambda function
Now that we have granted the Lambda function permissions to access the DynamoDB table, we can read and write data to the table. To do so, we need to use the boto3 library to interact with the DynamoDB table.
# filename: cdk_app/fn/index.py
import os
import boto3
import requests
dynamodb = boto3.resource("dynamodb")
# 👇🏽 get the table name from the environment variables
table_name = os.environ["TABLE_NAME"]
table = dynamodb.Table(table_name)
def handler(event, context):
response = requests.get("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1")
# 👇🏽 write the response to a file in the bucket
table.put_item(Key={"pk": "TODO", "sk": "1"}, Item={"data": response.json()})
# 👇🏽 read the file and send the contexts as response
stored_response = table.get_item(Key={"pk": "TODO", "sk": "1"})
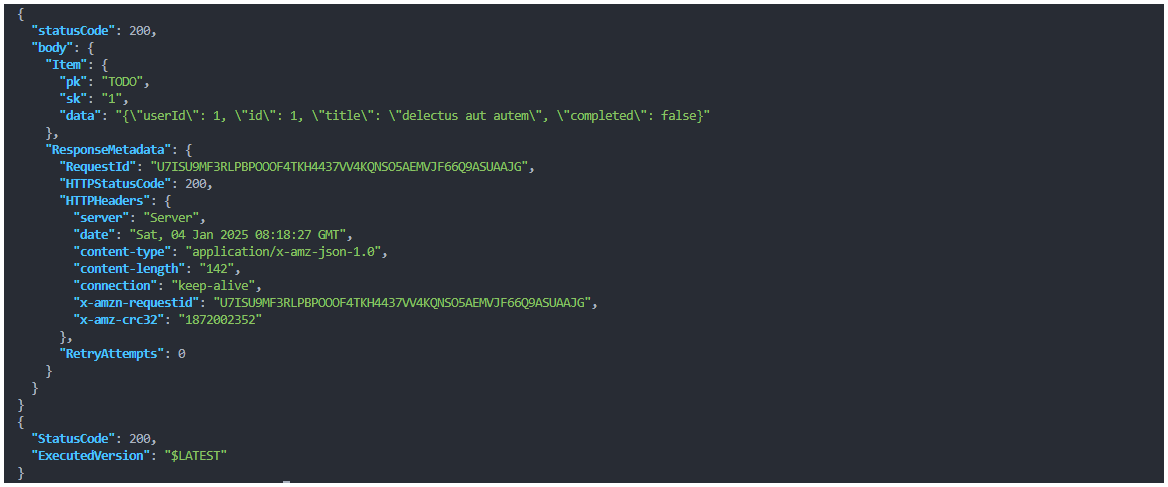
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": stored_response}
In the above code, we use the boto3 library to interact with the DynamoDB table. We first write the response from the API to a file in the bucket and then read the file and send the contents as a response. This method can be modified based on your exact use case.
Testing the Lambda function
To test the Lambda function we need its name. We can get the name of the lambda function from the stack output.
First list the stack outputs:
function_name=$(aws lambda list-functions --query "Functions[?contains(FunctionName, 'MyDynamoDBFunction')].[FunctionName]" --output text)
Then invoke the lambda function:
aws lambda invoke \
--function-name $function_name \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--payload '{ "key": "value" }' \
/dev/stdout | jq
Note
The jq command is used to format the JSON output. If you don't have it installed, you can install it by running brew install jq on macOS or apt-get install jq on Linux.
This will invoke the Lambda function and print the response in the terminal.