CDK API Gateway with Custom Domain
Let me begin by stating it took almost 3 weeks to figure this out and yet the AWS CDK Documentation on API Gateway is so bad, I was able to get everything working except the base_path. I do appreciate any pointers if you may have them.
If you know what API Gateway is, TL;DR jump to creating the API Gateway with CDK.
What is API Gateway?
API Gateway is a serverless service from AWS that helps you create API Endpoints which can be connected with other AWS services such as Lambda, Step Functions, etc.
API Gateway forms the foundation of serverless design that allows developers to create APIs that are infinitely scalable and easily connectable to other AWS services that are used to build serverless applications.
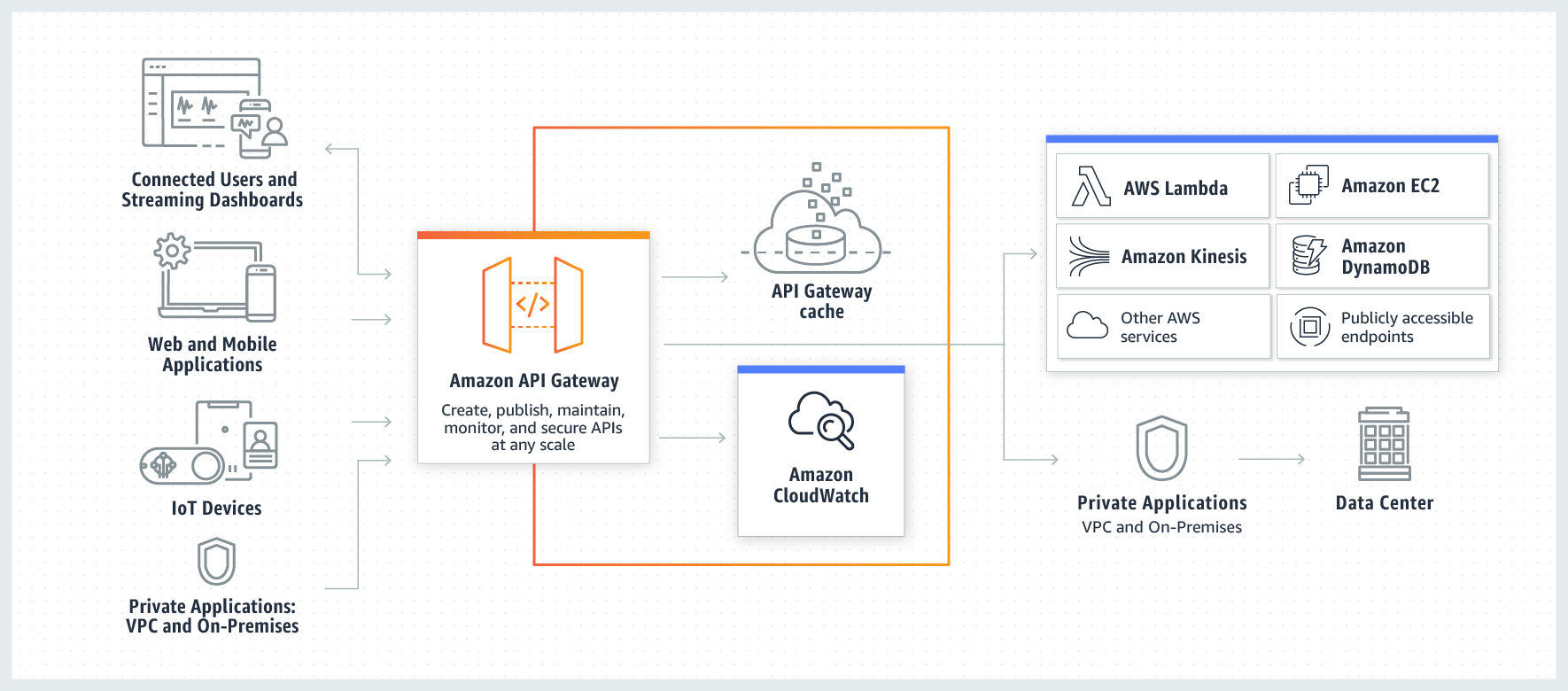
Users and consumers from around the globe can be given an app or a website that calls these APIs to authenticate users, and fetch data from the backend which can also be serverless giving massive cost savings and scalability.
API Gateway gives you the ability to create 3 types of APIs 1. REST APIs (part of API Gateway V1) 2. HTTP APIs (part of API Gateway V2) 3. Websockets APIs (part of API Gateway V2)
What is Route53?
Route53 is a DNS service from AWS that allows you to create custom domains and subdomains for your applications. It also allows you to register domains and manage DNS records for your domains.
Connect API Gateway to a custom domain
When you create an API Gateway, by default it provides you with a URL that looks like this
https://<api-id>.execute-api.<region>.amazonaws.com/<stage>
The API ID is a unique identifier for you API Gateway and is a random string of characters that changes every time you deploy your API Gateway. This is not ideal if you want to give the endpoint to your users or customers.
In these cases you would want to create a custom domain that is easy to remember.
To do so, you need to do the following
- Create a certificate in Amazon Certificate Manager (ACM) that maps to the domain you want to use. This step requires you to also create records in Route53 to verify domain ownership
- Create an API Gateway
- Attach the domain and certificate to the API Gateway
- Create an Route53 A record alias that maps to the domain
For this example I am going to use the sample domain example.com and map the API gateway to a custom domain api.example.com.
Pre-requisites
- You need to own a domain name registered with AWS Route53.
- Have AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) Installed
Create a new project
Open your terminal and create a new directory for your project
mkdir api_route53 && cd api_route53
Next create a new CDK Project by running the following command
cdk init app --language=python
Open the folder in VSCode
code .
You should see the following project structure already created
.
├── README.md
├── api_route53
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── api_route53_stack.py
├── app.py
├── cdk.json
├── requirements-dev.txt
├── requirements.txt
├── source.bat
└── tests
Finally, install the required dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Also install the following library - more on this later
pip install aws-cdk.aws-lambda-python-alpha
Initialise the Stack
Open the file api_route53/api_route53_stack.py and import the libaries we will need and initialise the stack
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 1
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_certificatemanager as acm,
aws_route53 as route53,
aws_apigateway as apigateway,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
aws_lambda_python_alpha as lambda_python,
aws_route53_targets as targets,
)
from constructs import Construct
class ApiRoute53Stack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# The code that defines your stack goes here
We have defined and initialised a stack named ApiRoute53Stack that will contain the definition of the environment we want to create.
Create the ACM Certificate
First we fetch the hosted zone for the domain we want to use.
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 2
hosted_zone = route53.HostedZone.from_lookup(self, "HostedZone", domain_name="example.com")
Next, let's create the certificate and validate it using DNS validation method.
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 3
certificate = acm.DnsValidatedCertificate(
self,
"ApiCertificate",
domain_name="api.example.com",
hosted_zone=hosted_zone,
region="us-east-1",
)
We have used us-east-1 to create the certificate because we intend to create edge-optimised API Gateway for which the certificate must be created in us-east-1. If you choose to create a regional API Gateway the certificate must reside in the region where API Gateway is created.
Create the lambla function
A) Create a new file api_route53/lambda_function.py and add the following code
# api_route53/lambda_function.py
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Hello from Lambda!')
}
B) Now back in the file api_route53/api_route53_stack.py we can create a lambda function that will be used by the API Gateway
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 4
# Create a lambda function
handler = _lambda.Function(
self,
"ApiHandler",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="lambda_function.lambda_handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("api_route53"),
)
Here we chose Python 3.10 as our runtime, and the handler is the function in the lambda file that will be called when the API Gateway is invoked. The code is loaded from the api_route53 directory.
Create the API Gateway
Now we create an api gateway and 1. Attach a lambda function to it 2. Add a domain_name to the API Gateway and map it to the certificate we created earlier
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 5
# Create an API Gateway
api = apigateway.LambdaRestApi(
self,
"ApiGateway",
handler=handler,
domain_name=apigateway.DomainNameOptions(
domain_name="api.example.com",
certificate=certificate,
security_policy=apigateway.SecurityPolicy.TLS_1_2,
endpoint_type=apigateway.EndpointType.EDGE,
)
)
Now keep in mind that API Gateway can have multiple Endpoints and creating the above domain_name property does not remove the default Endpoint in form on https://<api-id>.execute-api.<region>.amazonaws.com/<stage>, instead you will have two endpoints.
Create the Route53 A record
Finally, we create a Route53 A record that maps the domain to the API Gateway
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py :: Step 6
# Create a Route53 record
route53.ARecord(
self,
"ApiRecord",
record_name="api",
zone=hosted_zone,
target=route53.RecordTarget.from_alias(targets.ApiGateway(api)),
)
Deploy the stack
First we need to create the app by editing the ./app.py file
# app.py
import aws_cdk as cdk
from api_route53.api_route53_stack import ApiRoute53Stack
app = cdk.App()
env = cdk.Environment(account="<YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID>", region="us-east-1")
ApiRoute53Stack(app, "ApiRoute53Stack", env=env)
app.synth()
Finally, deploy the stack by running
cdk deploy
Test the API
You can test the API by running the following command
curl https://api.example.com/api
This should return the following response
Hello from Lambda!
Conclusion
The overall code for the API Stack is below. You can also find the code sample in this Github Repo
# api_route53/api_route53_stack.py
from aws_cdk import (
Stack,
aws_certificatemanager as acm,
aws_route53 as route53,
aws_apigateway as apigateway,
aws_lambda as _lambda,
aws_route53_targets as targets,
)
from constructs import Construct
class ApiRoute53Stack(Stack):
def __init__(self, scope: Construct, construct_id: str, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(scope, construct_id, **kwargs)
# The code that defines your stack goes here
# Fetch the hosted zone
hosted_zone = route53.HostedZone.from_lookup(self, "HostedZone", domain_name="taskman.click")
# Create a certificate
certificate = acm.DnsValidatedCertificate(
self,
"ApiCertificate",
domain_name="apix.taskman.click",
hosted_zone=hosted_zone,
region="us-east-1",
)
# Create a lambda function
handler = _lambda.Function(
self,
"ApiHandler",
runtime=_lambda.Runtime.PYTHON_3_10,
handler="lambda_function.lambda_handler",
code=_lambda.Code.from_asset("api_route53"),
)
# Create an API Gateway
api = apigateway.LambdaRestApi(
self,
"ApiGateway",
handler=handler,
domain_name=apigateway.DomainNameOptions(
domain_name="apix.taskman.click",
certificate=certificate,
security_policy=apigateway.SecurityPolicy.TLS_1_2,
endpoint_type=apigateway.EndpointType.EDGE,
)
)
# Create a Route53 record
route53.ARecord(
self,
"ApiRecord",
record_name="apix",
zone=hosted_zone,
target=route53.RecordTarget.from_alias(targets.ApiGateway(api)),
)