Create a Python virtual environment using venv
Python is the most popular programming language in the world. It Developers love it due to its versatility and the flexibility of using it in diverse ways. This is possible due to a plethora of Python packages published on PyPi and many others. There are so many Python packages that you almost can find a package to do something, as illustrated by my favourite web-comic, xkcd.
These packages or libraries can also depend on other packages, e.g. a very popular library used by data science professionals, Pandas, uses and builds on top of 3 other packages, Numpy, python-dateutil, and pytz.
The problem
But this diversity could also create problems for developers due to conflicts in the dependencies of multiple libraries, e.g. installing Pandas ends up installing 10+ other packages due. This could also cause conflicts between versions of dependencies.
Python Virtual Environment
This is where virtual environments can help. You can create different instances of Python specific for the application you're building without them conflicting with each other.
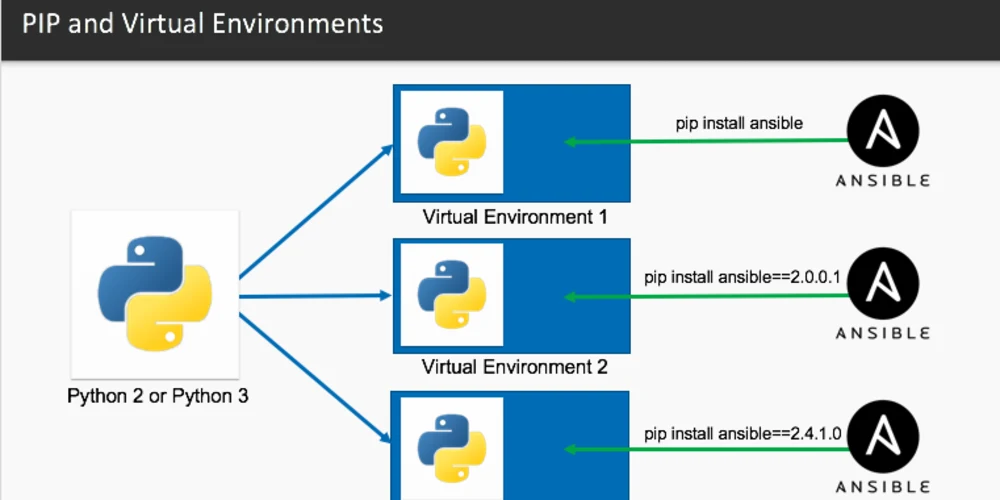
Create a virtual environment
Navigate to the folder that you want to place the virtual environment in and run venv module as shown below 👇🏽
python3 -m venv new-env
venvis the recommended module for managing virtual environments now andvirtualenvhas been deprecated by Python
This will create folder named new-env and place the virtual environment inside it including the Python interpreter, the standard library along with other supporting files.
Activate the virtual environment
After creating the virtual environment, you will need to activate it to be able to use it
On Windows, run:
new-env\Scripts\activate
On Unix or MacOS, run:
source new-env/bin/activate
Use the virtual environment
After creating the virtual environment, you will notice (new-env) in the terminal prompt you are using.
You can install any package using
python3 -m pip install <package-name>
If you have added the Python directory to path, you also use the below
pip install <package-name>
Deactivate the virtual environment
To deactivate, simply run
deactivate